The word carotenoid sounds complicated and “science-y,” but these nutrient compounds are a part of your everyday world—and thanks to their colorful pigments, they make that world a more colorful place.
The orange color in carrots and yams? That’s from carotenoids, especially beta-carotene. The pink in a flamingo, salmon and shrimp, and the red in a northern cardinal? Those colors also come from carotenoids. In fact, these red-pink colors often come from a lesser-known carotenoid called astaxanthin. But lesser known doesn’t mean less than!
Astaxanthin is one of the most versatile and valuable carotenoids found in nature. You won’t want to be without astaxanthin’s health benefits for your heart, your skin, your metabolism and even your longevity.
What is astaxanthin?
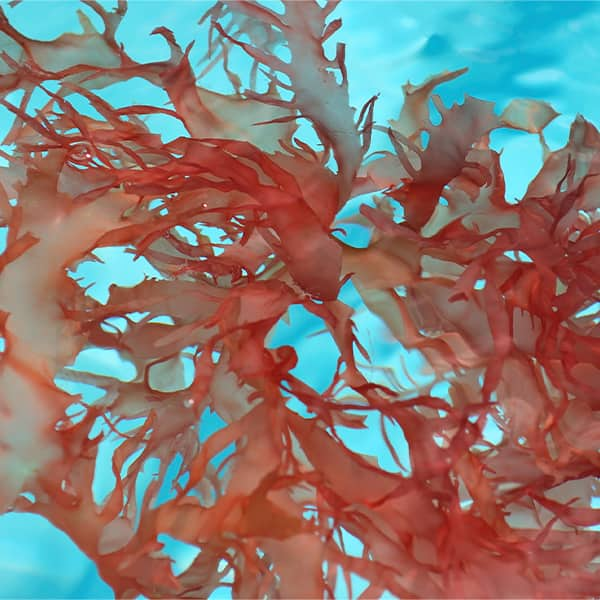
Astaxanthin belongs to the class of nutrient pigments known as carotenoids. Other members of this class include beta-carotene (sometimes seen written out as β-carotene), lutein & zeaxanthin and lycopene. Like other carotenoids, astaxanthin has powerful antioxidant properties.
Astaxanthin and other carotenoids give color to various plants and animals. But nothing to fear—if you get astaxanthin from food or supplements, you won’t change color! You might get a radiant youthful glow from all the health benefits you’ll receive, but you won’t take on a pink or salmon hue, we promise.
Although natural astaxanthin is present in so many plants and animals, the most concentrated naturally occurring source is the astaxanthin-producing microalgae (a really tiny freshwater plant in this case) Haematococcus pluvialis. Astaxanthin is extracted from this microalgae for use in supplements.
8 health benefits of astaxanthin
1. Astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant
Astaxanthin wears many hats. But many of the ways it can help our health boils down to its powerful antioxidant activity. Astaxanthin has a reputation of being one of the most powerful antioxidant nutrients. Astaxanthin’s antioxidant properties have a kind of ripple effect, since oxidative stress is believed to be one of the main culprits for negatively impacting your health, and is even a central player in aging itself.
Your eyes, skin, heart and immune system all need protection from oxidative stress (you might have heard it described as “free radicals”), and astaxanthin is there to help.
2. Astaxanthin is an eye health superstar

Carotenoids are famous for their role in eye health. They form an essential part of the protection of the retina of the eye (specifically the macula of the retina) against UV exposure.
Popular eye supplements that help protect aging vision often contain beta-carotene and lutein and zeaxanthin. But the most advanced eye health supplements will often add astaxanthin and another “cousin,” alpha-carotene. Astaxanthin’s role as an eye health powerhouse was confirmed in a study that showed that this carotenoid protected against eye strain in those working on visual displays. And with technology at our fingertips, anyone can benefit from taking astaxanthin—after all, who doesn’t have a little too much screen time these days?
3. Astaxanthin promotes youthful, supple skin
Beauty is more than skin deep, especially when it comes to your health. And in the case of your skin, making sure it stays youthful and vibrant can sometimes mean keeping the whole you healthy. This is the case with astaxanthin, which delivers whole-body health benefits while also supporting your skin health.
Astaxanthin protects against ultraviolet exposure—which can impact skin health and aging. One rigorous study in 23 healthy individuals found that 4 mg of astaxanthin per day protected against the oxidative stress caused by UV exposure. Astaxanthin even supported areas of skin that didn’t experience UV exposure—with those individuals experiencing smoother and more supple skin.
Another study conducted in 65 healthy women who used 6 or 12 mg of astaxanthin found that astaxanthin protected against the appearance of wrinkles and dryness. That’s not all—a different study found that 2 mg astaxanthin with 3 grams of a collagen preparation improved skin structure and integrity, and increased collagen production. The combination even promoted a healthy inflammatory response.
4. Astaxanthin keeps your heart healthy
When it comes to cardiovascular health, most of us need a little help to stay in tip-top shape. Even with everything we know nowadays about nutrition and being proactive, our heart and cardiovascular systems need to be in optimal working order to ensure a long, healthy life. And given everything else it can do, it’s not so surprising that one of astaxanthin’s most notable health benefits is that it really shines in the heart health department.
Much of this benefit comes down to astaxanthin’s superpower—its potent quashing of oxidative stress. But it has other benefits, too, like supporting healthy lipid levels. One study even found that it helped the heart pump more efficiently. Efficient pumping by the heart and supporting already-healthy blood pressure means blood and oxygen can get to all your tissues and cells.
5. Support your liver health with astaxanthin
Did you know your liver is one of the busiest places in your body? Of course, all that activity is microscopic, but there’s still a lot going on. In fact, the liver is indispensable to pretty much every metabolic and biochemical process in your body, including your inflammatory response and more. (Hey, we said it’s a lot!) And all that activity means things can sometimes go a little sideways. That can especially be the case if our metabolism isn’t working as efficiently as we would like.
Given astaxanthin’s growing list of ways it protects our health and fights valiantly against oxidative stress, it makes sense that it’s been scientifically studied for its role in supporting a healthy liver. And since the liver “touches” everything, a healthy liver means a healthy you.
6. Astaxanthin supports your immune system
We all want the best immune health we can manage, whether that means fighting off immune challenges or staying healthy and vital in our later years. Astaxanthin’s ability to support a healthy inflammatory response as well as to battle oxidative stress means it can be one of our best allies in maintaining immune health.
Moderate exercise is good for your immune system, but athletes often overdo it, making it harder to maintain a healthy immune response. However, in one study, astaxanthin helped preserve a healthy immune response in runners.
7. Astaxanthin protects metabolic health
At this point we wouldn’t blame you if you’re wondering “is astaxanthin good for everything?” It just might be, but we’ll stick with the areas where the evidence is solid. And that includes your metabolism—a broad term that relates to how your body processes foods into energy. And that, in turn, has a whole lot to do with the health of your blood vessels, your heart—and yes, your brain, too.
Metabolic health affects every cell and organ in the body, so it’s definitely an area you want to support with a healthy diet, staying active, prioritizing self-care (if you can…we know sometimes you’re the last one on your own “take care of” list!) and even taking astaxanthin. In a 12-week rigorous trial in 53 Japanese volunteers, astaxanthin supplementation at a dose of 12 mg daily supported multiple measures of healthy carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. (Astaxanthin, like other carotenoids, is a lipid-soluble nutrient.) A similar study in 50 individuals found astaxanthin also supports some healthy lipid metabolism measures.
8. Astaxanthin: a brain health supernutrient

Your brain is a wonder—you could say it runs the whole show. It’s also very delicate, which is probably why it’s encased in that hard bony shell we call our skull. But it’s also protected on the inside, by something called the blood-brain barrier. This microscopic barrier in the blood vessels of our brains is highly selective and can’t be penetrated by just anything. That’s in order to keep toxins and other unwanted substances out, but that also means it keeps certain nutrients out.
So, when a powerful antioxidant that can also support a healthy inflammatory response is found to cross the blood-brain barrier—meaning the body and brain welcome it—that’s a good sign that it’s good for brain-related health. Perhaps that’s why astaxanthin is the subject of scientific research involving optimizing brain function. One clinical study even found that a combination including astaxanthin and sesamin (an extract from sesame seeds) promoted comprehension and helped the study subjects perform complex tasks quickly and accurately.
Do astaxanthin supplements work?
Astaxanthin as a supplement works for all the properties and benefits we’ve just discussed. However, as is true for all nutrition and lifestyle and dietary supplements, don’t expect the results to be immediate. Proper nutrition takes time. Achieving optimal cardiovascular health can take months and years. Your skin won’t suddenly appear smooth and supple overnight as soon as you take astaxanthin. But yes, astaxanthin supplements work, and you can feel secure in the knowledge that astaxanthin in this form is a great science-based way to optimize your wellness.
Speaking of anti-aging and longevity supplements, if you’re still not sure what you need, a longevity quiz can help point you in the right direction and provide personalized recommendations of what to take for a long, healthy life.
How to take astaxanthin supplements
Take astaxanthin supplements the same way you’d take any food-based supplement—with a meal. Since carotenoids are fat soluble, like vitamin E and vitamin K, astaxanthin is absorbed best when taken with food.
Pro tip: Look for an astaxanthin supplement that is formulated with phospholipids to ensure optimal absorption. And as an added bonus, phospholipid formulas can be taken with or without food—making it even easier to take astaxanthin!
Can I take resveratrol with astaxanthin?
Both astaxanthin and resveratrol are naturally-occurring powerful antioxidants, and both have been studied for their anti-aging and longevity-promoting effects. You don’t need to take them at the same time, but you can if that’s easier for you. Taking both would definitely help optimize your health regimen!
References:
- Choi, Hye Duck, et al. “Positive effects of astaxanthin on lipid profiles and oxidative stress in overweight subjects.” Plan Foods Hum Nutr. November 2011. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21964877/
- Heidari, Marzieh, et al. “Effects of Astaxanthin supplementation on selected metabolic parameters, anthropometric indices, Sirtuin1 and TNF-α levels in patients with coronary artery disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.” Front Nutr. March 2023. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2023.1104169/full
- Ito, Naoki, et al. “Effects of Composite Supplement Containing Astaxanthin and Sesamin on Cognitive Functions in People with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.” J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29614679/
- Ito, Naoki, et al. “The Protective Role of Astaxanthin for UV-Induced Skin Deterioration in Healthy People-A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.” Nutrients. June 2018. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29941810/
- Neiman, David C., et al. “Astaxanthin supplementation counters exercise-induced decreases in immune-related plasma proteins.” Front. Nutr. March 2023. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2023.1143385/full
- Ni, Yinhua, et al. “Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E.” Sci Rep. November 2015. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26603489/
- Patil, Apurva D., et al. “Pharmaceutical and nutraceutical potential of natural bioactive pigment: astaxanthin.” Natural Products and Bioprospecting. December 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9259778/
- Sekikawa, Takahiro, et al. “Effects of diet containing astaxanthin on visual function in healthy individuals: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel study.” J Clin Biochem Nutr. January 2023. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36777084/
- Si, Pan, et al. “Biological and neurological activities of astaxanthin (Review).” Molecular Medicine Reports. August 2022. https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/mmr.2022.12816/abstract
- Tominaga, Kumi, et al. “Protective effects of astaxanthin on skin deterioration.” J Clin Biochem Nutr. July 2017. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28751807/
- Urakaze, Masaharu, et al. “The Beneficial Effects of Astaxanthin on Glucose Metabolism and Modified Low-Density Lipoprotein in Healthy Volunteers and Subjects with Prediabetes.” Nutrients. December 2021. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/12/4381
- Yoon, Hyun-Sun, et al. “Supplementating with dietary astaxanthin combined with collagen hydrolysate improves facial elasticity and decreases matrix metalloproteinase -1 and -12 expression: a comparative study with placebo.” J Med Food. July 2014. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24955642/





